How do humans affect the marine environment?
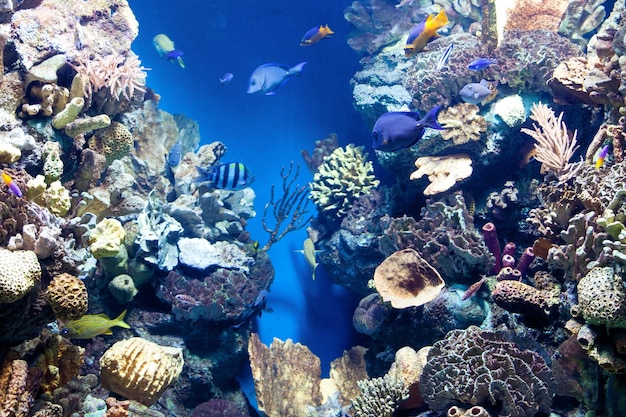
The marine environment is a fragile ecosystem that plays a crucial role in the health of our planet. However, human activities have had a significant impact on these delicate ecosystems. From pollution to overfishing, our actions have led to negative consequences for marine life and the overall health of our oceans.
Pollution
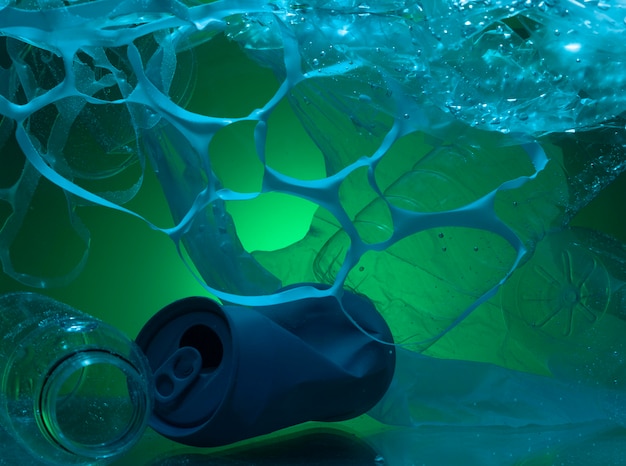
One of the most significant ways humans affect the marine environment is through pollution. Pollution comes in various forms, including oil spills, plastic waste, chemical runoff, and sewage discharge. These pollutants have devastating effects on marine life, leading to habitat destruction, water contamination, and the death of countless animals. Marine organisms can ingest or become entangled in debris, causing harm, and disrupting the food chain.
“The ocean is our planet’s life support system, and our actions are pushing it to the brink.” – Dr. Sylvia Earle
Overfishing
Overfishing is another major threat to the marine environment. As the demand for seafood continues to rise, commercial fishing fleets have depleted fish populations beyond sustainable levels. This has severe consequences for marine ecosystems, as it disrupts the balance of predator-prey relationships and can lead to the collapse of entire fish stocks. Overfishing also harms other species, such as seabirds and marine mammals, that rely on fish for their survival.
Climate Change
Climate change is having a profound impact on the marine environment. Rising global temperatures result in the warming of ocean waters and the melting of polar ice caps. These changes have severe consequences for marine life, including coral bleaching, ocean acidification, and habitat loss. Coral reefs, often referred to as “rainforests of the sea,” are particularly vulnerable to the effects of climate change, with many already experiencing mass die-offs.
“The oceans are the planet’s largest habitat. We need to recognize the impact of climate change on the ocean and take action to mitigate it.” – Jean-Michel Cousteau
Invasive Species
Human activities, such as shipping and the introduction of non-native species, have led to the spread of invasive species in marine environments. These invasive species can outcompete native species for resources, disrupt fragile ecosystems, and even cause extinctions. The ballast water discharged from ships is a significant means of introducing invasive species to new areas, as it often contains the larvae or eggs of marine organisms.
Tourism and Recreation
While tourism and recreation can provide economic benefits to coastal communities, they can also have negative impacts on the marine environment. Improper waste management, destruction of habitats for infrastructure development, and disturbance to marine life through activities like boating and snorkeling can all harm delicate marine ecosystems. It is essential for these industries to embrace sustainable practices to minimize their ecological footprint.
In conclusion, human activities have significantly affected the marine environment, threatening the health and biodiversity of our oceans. Pollution, overfishing, climate change, the introduction of invasive species, and unsustainable tourism practices all contribute to this problem. It is crucial for individuals, industries, and governments to recognize these impacts and take immediate action to protect and restore our marine ecosystems for future generations.
How can we save marine life?
1. Reduce plastic waste
Plastic pollution is a major threat to marine life. By reducing our use of single-use plastics, we can help protect the oceans and the creatures that inhabit them. Using reusable bags, water bottles, and straws can make a significant difference in reducing plastic waste.
2. Support sustainable fishing practices
Overfishing is a significant problem that affects marine ecosystems worldwide. Supporting sustainable fishing practices, such as buying seafood with eco-labels or from certified sustainable fisheries, helps ensure the long-term health of fish stocks and protects marine life.
3. Practice responsible boating
When boating, it is essential to be mindful of marine life. Be cautious of your speed to prevent collisions with marine mammals, such as dolphins or whales. Avoid areas with coral reefs or seagrass beds to prevent damage to these fragile ecosystems.
4. Create marine protected areas
Establishing marine protected areas (MPAs) helps conserve and restore marine ecosystems. These areas provide a safe haven for marine species to breed, feed, and rest without disturbance. They also help maintain biodiversity and promote overall ecosystem health.
5. Educate others about marine conservation
Spreading awareness about the importance of marine conservation is crucial. By educating others about the threats faced by marine life and the steps they can take to make a difference, we can inspire positive change and encourage more people to get involved.
6. Reduce carbon emissions
Climate change poses a severe threat to marine ecosystems. Rising sea temperatures and ocean acidification harm corals, fish, and other marine organisms. By reducing our carbon footprint through energy conservation and supporting renewable energy sources, we can help mitigate these impacts.
7. Support organizations working on marine conservation
Many organizations dedicate their efforts to protect and conserve marine life. Supporting these organizations through donations or volunteering can make a significant impact. They work on research, conservation initiatives, and advocacy to safeguard the oceans and the creatures that rely on them.
8. Promote responsible tourism
Tourism can have both positive and negative impacts on marine ecosystems. Choosing responsible tour operators and adhering to guidelines, such as not touching or disturbing marine life, helps minimize the negative impacts of tourism and preserves the natural beauty of marine environments.
9. Participate in beach cleanups
Participating in beach cleanups is an effective way to remove trash and debris that can harm marine life. By organizing or participating in these events, we can prevent plastic and other pollutants from entering the ocean and endangering marine animals.
10. Support research and conservation efforts
Research plays a vital role in understanding and conserving marine life. Supporting scientific research initiatives and conservation projects helps expand our knowledge and contribute to long-term conservation strategies.
How do we use marine environments?
Fishing and Aquaculture
Marine environments play a crucial role in supporting the fishing industry and aquaculture. Fishing provides a source of livelihood to millions of people around the world. It not only provides food but also contributes to economic growth. Aquaculture, on the other hand, involves the cultivation of fish, shellfish, and other marine organisms in specially designed areas such as fish farms and hatcheries. This helps meet the growing demand for seafood.
Tourism and Recreation
Marine environments are popular destinations for tourists and recreational activities. Coastal regions with beautiful beaches, coral reefs, and stunning marine life attract millions of visitors each year. Activities such as snorkeling, scuba diving, sailing, and boating provide people with an opportunity to explore and appreciate the marine ecosystems.
Shipping and Transportation
The marine environment is essential for shipping and transportation. Oceans and seas serve as major transportation routes, facilitating trade and commerce between countries. Ships transport goods, raw materials, and resources across continents. Additionally, cruise ships offer leisure travel experiences, allowing people to explore different destinations while enjoying the amenities on board.
Energy Production
Marine environments also contribute to energy production. Offshore wind farms harness the power of wind to generate electricity, reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Tidal and wave energy technologies utilize the kinetic energy of tides and waves respectively to produce clean, renewable energy. These advancements help in reducing carbon emissions and combating climate change.
Scientific Research
Marine environments are invaluable for scientific research. Scientists study various aspects of marine life, including biodiversity, ecosystems, and climate patterns, to better understand our planet. Research conducted in marine environments helps identify new species, discover potential medicinal compounds, and monitor the effects of human activities on the ecosystem.
Waste Disposal
Marine environments are unfortunately often used as dumping grounds for waste disposal. This includes untreated sewage, industrial waste, and plastic pollution. Such practices have detrimental effects on marine life and the overall health of the ecosystem. Proper waste management strategies and increased awareness are necessary to protect and preserve marine environments.
Ecosystem Services
Marine environments provide invaluable ecosystem services that benefit humans and the planet. These include carbon sequestration, water filtration, and shoreline protection. Coral reefs, for example, act as natural barriers, protecting coastlines from storms and erosion. Protecting and restoring these ecosystems is essential for maintaining the balance of our natural environment.
In conclusion, marine environments are utilized in various ways such as fishing, aquaculture, tourism, shipping, energy production, scientific research, waste disposal, and providing ecosystem services. It is crucial to manage these activities sustainably to ensure the long-term viability and health of our marine ecosystems. As individuals, we can contribute by practicing responsible tourism, supporting sustainable fishing practices, and reducing our use of single-use plastics.
How can we improve marine biodiversity?
Marine biodiversity refers to the variety of life forms in oceans, seas, and other marine environments. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the health and balance of marine ecosystems. However, due to human activities and climate change, marine biodiversity is under threat. Here are some ways we can work towards improving marine biodiversity:
1. Promoting sustainable fishing practices
Overfishing is a major threat to marine biodiversity. Implementing measures such as setting catch limits, promoting responsible fishing techniques, and establishing marine protected areas can help conserve fish populations and their habitats.
2. Reducing pollution
Pollution from land-based activities, such as agricultural runoff and industrial waste, negatively impacts marine life. Implementing stricter regulations, promoting recycling and waste management, and reducing the use of single-use plastics can help minimize pollution and its effects on marine biodiversity.
3. Creating marine protected areas
Marine protected areas (MPAs) are designated areas where human activities are restricted to preserve marine ecosystems. MPAs provide refuge for marine species and help restore depleted populations. Governments and organizations should work together to establish more MPAs.
4. Promoting sustainable tourism
Tourism can have both positive and negative impacts on marine biodiversity. By promoting sustainable tourism practices, such as responsible snorkeling and diving, respecting marine wildlife, and supporting local conservation efforts, we can minimize the negative effects and help protect marine ecosystems.
5. Raising awareness and education
Increasing public awareness about the importance of marine biodiversity is crucial. Education programs, public campaigns, and initiatives to engage communities in marine conservation can play a significant role in fostering a sense of responsibility towards protecting marine life.
6. Restoring and preserving coastal habitats
Coastal habitats, such as mangroves, seagrasses, and coral reefs, are vital for marine biodiversity. Efforts should be made to restore and protect these habitats from destruction caused by coastal development, pollution, and climate change.
7. Addressing climate change
Climate change is a significant threat to marine biodiversity as it leads to ocean acidification, rising sea temperatures, and sea level rise. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions, promoting renewable energy sources, and supporting research on climate change impacts can help mitigate its effects on marine ecosystems.
8. Supporting sustainable aquaculture
Aquaculture, or fish farming, has the potential to reduce pressure on wild fish populations. However, it must be done sustainably to minimize negative impacts on marine biodiversity. Promoting best practices, minimizing antibiotic use, and developing eco-friendly aquaculture techniques are essential in this regard.
9. Engaging in conservation partnerships
Collaboration among governments, NGOs, scientists, and local communities is crucial for effective marine biodiversity conservation. Establishing partnerships and sharing knowledge and resources can lead to more comprehensive and impactful conservation efforts.
10. Monitoring and research
Regular monitoring and research are essential to understand the status of marine biodiversity and the effectiveness of conservation measures. By investing in scientific research and monitoring programs, we can gather valuable data and make informed decisions to improve marine biodiversity.
How can we stop habitat loss in the ocean?
Habitat loss in the ocean is a major concern and has detrimental effects on marine life. It is important for us to take action and implement measures to protect these habitats. Here are some ways we can stop habitat loss in the ocean:
1. Establish marine protected areas:
Creating marine protected areas (MPAs) is crucial in conserving ocean habitats. MPAs help preserve biodiversity, protect fish populations, and promote the recovery of damaged ecosystems. By designating specific areas as protected, we can prevent destructive activities such as fishing or mining that harm marine habitats.
2. Reduce plastic pollution:
Plastic pollution poses a significant threat to ocean habitats. To combat this problem, we should reduce our use of single-use plastics and promote recycling. Proper disposal of plastics and raising awareness about the importance of keeping our oceans clean are also essential steps in stopping habitat loss.
3. Promote sustainable fishing practices:
Overfishing is a major contributor to habitat loss in the ocean. Implementing sustainable fishing practices, such as enforcing catch limits and using selective fishing methods that minimize bycatch, can help protect marine habitats and ensure the long-term viability of fish populations.
4. Enhance coastal zone management:
Coastal zones are critical habitats that support a wide range of marine species. Improving coastal zone management by enforcing regulations, reducing pollution from coastal development, and implementing erosion control measures can help protect these vital habitats.
5. Support coral reef conservation:
Coral reefs are highly sensitive and diverse ecosystems that are under threat from factors like rising sea temperatures and ocean acidification. Supporting organizations and initiatives dedicated to coral reef conservation is crucial in preserving these habitats for future generations.
6. Educate and raise awareness:
Educating the public about the importance of ocean habitats and the threats they face is essential. By raising awareness through educational campaigns and initiatives, we can encourage individuals and communities to take action and make sustainable choices that help protect marine ecosystems.
7. Collaborate with international organizations:
Habitat loss in the ocean is a global issue that requires international cooperation. Working together with international organizations, governments, and NGOs can help develop effective strategies and policies to stop habitat loss and ensure the long-term health of our oceans.
8. Support research and monitoring efforts:
Continued research and monitoring of ocean habitats are crucial in understanding the impact of human activities and identifying effective conservation strategies. Supporting scientific research and initiatives that focus on ocean conservation can contribute to the prevention of habitat loss.
9. Encourage sustainable tourism practices:
Tourism can have both positive and negative impacts on ocean habitats. Promoting sustainable tourism practices that minimize the disturbance to marine ecosystems, educate visitors about conservation, and contribute to local community development can help protect ocean habitats.
10. Advocate for stronger legislation:
Advocacy plays a vital role in stopping habitat loss in the ocean. By supporting and advocating for stronger legislation and regulations that protect marine habitats, we can create a legal framework that ensures the preservation of these important ecosystems.